The colonoscopy is a medical procedure during which a long flexible tube is used to look inside the colon. It is a procedure performed by a gastroenterologist, a well-trained specialist. The colonoscope is a long, thin, flexible tube with a tiny video camera. By adjusting the various controls on the colonoscope, the gastroenterologist can carefully guide the instrument in any direction to look at the inside of the colon. The high-quality picture from the colonoscope is shown on a TV monitor, and gives a clear, detailed view.
Education
- Home
- Education
-
+ 생로병사의 비밀 E540 150401 쉬쉬하지 말자, 방광 질환/골다공증 약이 턱뼈 괴사증을 일으킨다
-
+ 비타민 E576 150401 조용한 살인자, 대장암
-
+ COLONOSCOPY
Colonoscopy
Reason for a Colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy is an important way to check for colon cancer and to treat colon polyps. Polyps are abnormal growths on the inside lining of the intestine; they vary in size and shape and while most polyps are not cancerous, some may turn into cancer. However, it is not possible to tell just by looking at a polyp if it is malignant or potentially malignant. This is why colonoscopy is often used to remove polyps, a technique called a polypectomy.
- Colonoscopy is also a safe and effective way to evaluate problems such as: Blood loss. Abdominal or rectal pain. Changes in bowel habits, such as chronic diarrhea. Active bleeding from the large bowel.
- These may be used to painlessly remove a suspicious-looking growth or to biopsy, that is, take a small piece of tissue for further analysis. In this way, colonoscopy may help to avoid surgery or to better define what type of surgery may need to be done.
Before the Procedure
- Be sure to let your doctor know a complete list of all the medicines you are taking including over-the-counter medications and natural supplements and any allergies you have to drugs or other substances.
- If you have heart, lung or other medical conditions that may need special attention before, during or after the colonoscopy. It is especially important to discuss the taking of diabetic medications and anticoagulants (sometimes called blood thinners) with your physician before the test.
- Prepare Your Colon for the Test You will be given instructions in advance that will outline what you should and should not do in preparation for colonoscopy; be sure to read and follow these instructions. One very critical step is to thoroughly clean out the colon, which, for many patients, can be the most trying part of the entire exam. It is essential that you complete this step carefully, because how well the bowel is emptied will help determine how well your doctor can examine it during colonoscopy.
- Check your instructions about what to eat or drink the night before your colonoscopy and when to stop eating. Consult your doctor prior to the procedure to determine if the medications you are on should be taken or not prior to the colonoscopy.
After Colonoscopy
- Plan to rest for the remainder of the day after your colonoscopy. This means not driving, so you will need to arrange to have a family member or friend take you home.
- Occasionally, minor problems may persist, such as bloating, gas or mild cramping, which should disappear in 24 hours or less.
-
+ Thyroid ultrasound & Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
What is a thyroid nodule?
A thyroid nodule is a lump or growth that has been formed within your thyroid. This lump is formed from an abnormal growth of thyroid cells. While most nodule formations are diagnosed as benign (noncancerous), a small percentage can be malignant (cancerous).
Thyroid Ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is a vital tool used for nodule evaluation to help identify suspicious vs benign nodules. An ultrasound will produce images of the thyroid by bouncing high-frequency sound waves off of the gland. It is not radiation. It can show what the nodules look like, the size of the nodules, and their location within the thyroid gland. There are specific characteristics that can be seen with an ultrasound machine including:
- If the nodule is solid, cystic (fluid- filled), or complex (both solid and cystic)
- If the nodule shows calcification, or irregular shape or vascularity.
Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
A fine needle aspiration biopsy ( FNABx) is a common and simple procedure used to sample thyroid nodules and determine whether they are cancerous. The procedure is done in the office, under ultrasound guidance to ensure sample accuracy. A very fine needle is used to attain a tissue sample from the nodule in question, and samples are sent to pathology for evaluation. The results are usually available within two weeks. Results will indicate whether the nodule is benign, non-diagnostic, atypical/suspicious, or malignant. While the vast majority of thyroid nodules are benign, small percentages do contain thyroid cancer. FNA biopsy is the best way to determine what your course of action should be.
Advantages of FNA bx
- Few complication
- High diagnostic accuracy
- Cost effective
- No stitches and no scarring
- Reduces anxiety and patients are able to resume normal activities
- Preliminary results obtained quickly and clinicians notified within one hour of procedure, usually within 20 minutes.
-
+ EGD Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
What is an EGD?
Upper GI endoscopy is a procedure performed by a gastroenterologist, a well-trained specialist who uses the endoscope to diagnose and, in some cases, treat problems of the upper digestive system. The endoscope is a long, thin, flexible tube with a tiny video camera and light on the end. By adjusting the various controls on the endoscope, the gastroenterologist can safely guide the instrument to carefully examine the inside lining of the upper digestive system. The high-quality picture from the endoscope is shown on a TV monitor; it gives a clear, detailed view. EGD can be helpful in the evaluation or diagnosis of various problems, including difficult or painful swallowing, pain in the stomach or abdomen, and bleeding, ulcers and tumors. Tiny instruments can be passed through an opening in the endoscope to obtain tissue samples, coagulate (stop) bleeding sites, dilate or stretch a narrowed area, or perform other treatments.
Before Procedure
- Be sure to let your doctor know a complete list of all the medicines you are taking— including any over-the-counter medications and natural supplements — and any allergies to drugs or other substances.
- Your medical team will also want to know if you have heart, lung or other medical conditions that may need special attention before, during or after an upper GI endoscopy.
- It is important they know if you are taking diabetic medications or anticoagulants (sometimes called blood thinners) or have bleeding or clotting problems.
- The stomach must be empty for the best possible examination. Do not take anything by mouth for the eight hours before the examination. Food in the stomach will block the view through the endoscope and it could cause vomiting.
- A companion must accompany you to the examination because you will be given medication to help you relax. It will make you drowsy, so you will need someone to take you home. You will not be allowed to drive for the rest of the day after the procedure. You should not plan to return to work or perform activities that require full alertness for the remainder of the day. Even though you may not feel tired, your judgment and reflexes may not be normal.
After procedure
- You will be kept in the endoscopic area until most of the effects of the medication have worn off.
- You may feel a little bloated for a short time after the examination because of air that is put into the stomach. Your throat may be a little sore for a while after the EGD, although this is unusual.
- Localized irritation of the vein may occur at the site of medication injection. A tender lump develops which may remain for several weeks but goes away eventually.
- Bleeding may occur from the site of biopsy or polyp removal. It is usually minimal.
- You will be able to resume your diet after the EGD unless you are instructed otherwise.
- Your examination will be discussed with you before you leave.
- Complications rarely occur. These include perforation, puncture of the intestinal wall that could require surgical repair, and bleeding.
-
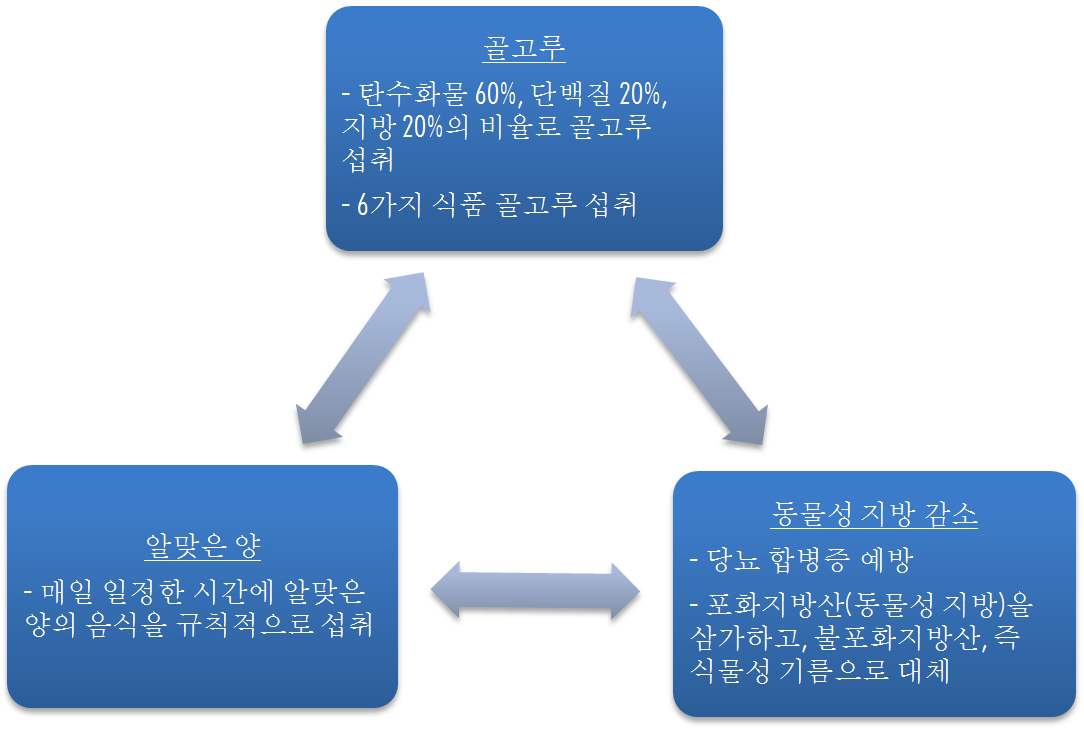
+ 당뇨병 식이요법의 기본원칙
- 매일 일정한 시간에 알맞은 양의 음식을 규칙적으로 먹습니다.
- 혈당을 안정시키기 위해서는 식사 시간과 양을 가능한 매일 일정하게 하는것이 중요합니다.
- 설탕이나 꿀 등 단순당의 섭취를 주의합니다.
- 단순당은 농축된 열량원이며, 소화흡수가 빨라 혈당상승을 촉진시킵니다.
<주의 식품>: 설탕, 사탕, 꿀, 엿, 잼, 초콜릿, 과일 통조림, 젤리, 유색우유, 가당연유 및 설탕 입힌 플레이크 등.
- 식이섬유소를 적절히 섭취합니다.
- 식이섬유소는 혈당과 혈종지방의 농도를 낮추므로 혈당조절과 심장순환계 질환의 예방에 도움이 됩니다.
<식이섬유 식품>: 잡곡밥, 현미밥, 채소, 과일, 콩류, 견과류 및 녹황색 채소 등.
- 지방을 적정량 섭취하며 콜레스테롤의 섭취를 제한합니다.
- 동물성 지방 및 콜레스테롤은 심혈관계 질환의 위험을 증가킬 수 있으므로 가급적 섭취를 줄이고 식물성 기름으로 적정량 섭취합니다.
<불포화 지방 식품>: 등푸른 생선, 올리브유, 카놀라유 및 호두 등.
- 소금 섭취를 줄입니다.
- 과다한 소금섭취는 혈압을 상승시킬 수 있으므로 싱겁게 먹는 습관을 갖도록 합니다.
- 술은 피하는 것이 좋습니다
- 술은 영양소가 포함되지 않으면서 열량을 많이 내므로 피하는 것이 좋습니다.
당뇨병 식이요법의 기본원칙